Essential Soldering Iron Projects for Electronic Hobbyists
Introduction
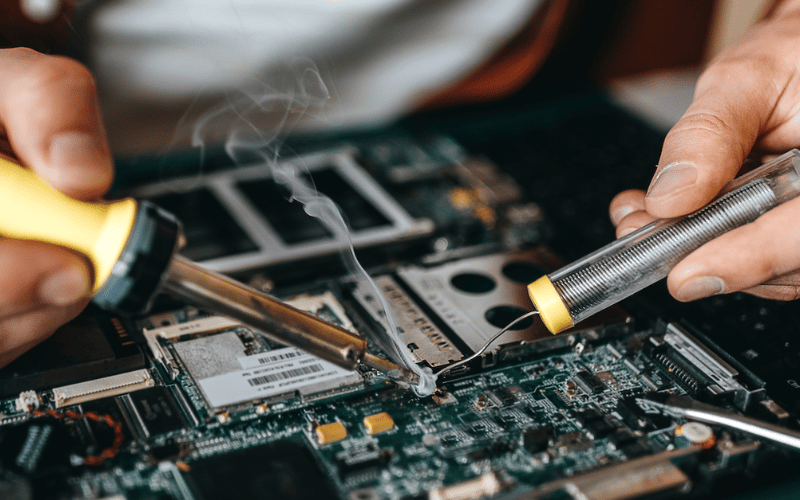
Welcome to the exciting world of soldering iron projects for electronic hobbyists! Whether you’re a beginner looking to dive into the realm of DIY electronics or an experienced tinkerer seeking new challenges, this comprehensive guide is designed to inspire and guide you through the art of soldering. From understanding the basics of soldering iron to mastering advanced techniques and creating intricate projects, this article will provide valuable insights, expert tips, and safety precautions to help you unlock the full potential of your soldering skills.
Understanding Soldering Irons
What is a soldering iron?
A soldering iron is a hand tool used in soldering to heat metals and create a bond between them. It consists of a heated metal tip and an insulated handle, allowing precise application of heat to melt solder and join metal components together. Soldering irons are essential for assembling circuits, repairing electronics, and building various electrical and electronic projects.
Types of soldering irons
- Pencil irons: Pencil irons are the most basic type of soldering irons. They are lightweight, compact, and ideal for delicate electronic soldering tasks. The slim design and fine tip make them perfect for working with small electronic components such as circuit boards, wires, and integrated circuits.
- Soldering stations: Soldering stations are versatile tools that offer adjustable temperature settings, ergonomic designs, and enhanced safety features. They are suitable for a wide range of soldering applications, from hobbyist projects to professional electronics repair. The adjustable temperature control allows users to optimize the heat for different soldering tasks, while the ergonomic design ensures comfort during prolonged use.
- Temperature-controlled irons: Temperature-controlled irons provide precise heat regulation and advanced thermal management. These irons are essential for intricate electronic projects that require accurate temperature control to prevent damage to sensitive components. The ability to maintain a consistent temperature throughout the soldering process makes them indispensable for professional electronics manufacturing and repair.
Essential Tools for Soldering Iron Projects
Soldering iron tips and flux
- Soldering Iron Tips:
- It’s crucial to understand the different shapes of soldering iron tips and how they affect soldering. Here are some key tips shapes:
- Chisel tip: Ideal for large soldering applications and heat transfer to larger areas.
- Conical tip: Suited for precision work and soldering small components with accuracy.
- Bevel tip: Provides a good balance between precision and heat transfer for general soldering tasks.
- Flux:
- Flux is a vital component in achieving high-quality soldered joints. It serves the following purposes:
- Promoting solder flow: By reducing the oxidation of metals, flux facilitates the flow of solder onto the joint, leading to stronger and more reliable connections.
- Enhancing bond strength: Flux helps in promoting better adhesion between the solder and the metals being joined, resulting in durable soldered joints.
Solder wire and soldering stand
When it comes to soldering, having the right tools is crucial for achieving professional results. Let’s dive deeper into the significance of high-quality solder wire and a reliable soldering stand:
- Solder Wire: Utilizing high-quality solder wire is essential for producing clean and reliable soldered connections. A premium solder wire with the appropriate flux core can significantly improve the efficiency of the soldering process. It ensures optimal wetting and bonding, resulting in durable and long-lasting connections.
- Soldering Stand: A sturdy soldering stand is more than just a resting place for the soldering iron. It provides a stable base, which is crucial for safely holding the soldering iron when not in use. It also offers a convenient and secure place to hold the iron during intricate soldering tasks, preventing accidental burns or damage to work surfaces.
Heat-resistant tools and safety gear
When working with hot soldering irons, having the right heat-resistant tools and safety gear is crucial for both efficiency and personal safety. Here are some key items to consider:
- Helping Hands: A useful tool for holding circuit boards, wires, and small components in place when soldering. This ensures stability and precision during intricate soldering work.
- Tweezers: Fine-pointed tweezers are ideal for handling small electronic components, placing them accurately, and removing excess solder.
- Clamps: Different types of clamps, such as third-hand tools or PCB holder vices, are essential for securing circuit boards and preventing movement while soldering.
Moreover, an assortment of heat-resistant gloves is indispensable for protecting hands from direct contact with hot components as well as hot soldering irons. Safety glasses with heat-resistant properties are also essential to safeguard against potential eye injuries due to solder spatters or flying debris. When selecting safety gear, make sure to choose items that are specifically designed for soldering and electrical work, ensuring they meet relevant safety standards.
Basic Soldering Techniques
Tinning wires and components
Tinning is the process of coating wires and components with a thin layer of solder to prevent oxidation and facilitate soldering. It involves heating the surfaces and applying solder to form a protective layer, ensuring strong and reliable electrical connections.
- Importance of Tinning:
- Tinning prevents oxidation and corrosion of wires and components, ensuring their longevity.
- Facilitates soldering by providing a smooth surface with good solder wetting properties.
- Creates durable and reliable electrical connections, essential for the functionality of electronic circuits.
- Steps for Tinning Wires and Components:
- Cleaning: Before tinning, it’s important to clean the surfaces of wires and components to remove any contaminants or oxidation.
- Flux Application: Applying flux aids in the soldering process by removing oxides and promoting solder adhesion.
- Preheating: Heating the surfaces before solder application ensures proper wetting and adhesion of the solder.
- Solder Application: The process of carefully applying the solder to form a protective and conductive layer on the surfaces.
- Types of Solder Used for Tinning:
- Lead-based solders:
- Traditional choice with good wetting properties; however, environmental concerns have led to their reduced usage.
- Lead-free solders:
- Environmentally friendly alternatives, commonly used in modern electronics manufacturing.
Creating strong and clean joints
Creating strong and clean joints is crucial for ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of circuitry. By employing precise heat application and solder flow, engineers can produce consistent and reliable connections. However, it is equally important to be mindful of the potential pitfalls that can compromise the integrity of these joints.
- Factors affecting joint strength:
- Choice of solder material and flux
- Adequate preparation of surfaces to be joined
- Proper heat control and duration
- Common issues and their solutions:
- Excess Solder: Overabundance of solder can lead to bridging and poor electrical conductivity. It is essential to use the appropriate amount of solder and to remove any excess with a desoldering braid or pump.
- Cold Joints: Inadequate heat application can result in cold joints, characterized by poor adhesion and mechanical strength. Reheating the joint and ensuring proper solder flow can rectify this issue.
- Testing: Verification of joint integrity through resistance and continuity tests is essential for confirming the quality and reliability of the connections.
Desoldering old components
Desoldering is a crucial skill in electronics that involves the careful removal of old components and solder from circuit boards. This process is essential for making repairs, salvaging components, or modifying existing circuitry. Here’s a more detailed look at desoldering:
- Tools and Equipment: Utilizing the right desoldering tools, such as a soldering iron with a vacuum or desoldering braid, is vital for successful desoldering. These tools help in applying heat to the existing solder and effectively removing it from the circuit board.
- Removing Components: Before desoldering, it’s important to identify the components that need to be removed. Carefully heating the solder joints and using a desoldering pump or braid, you can extract the components while minimizing damage to the circuit board.
- Cleanup and Inspection: After removing the old components, it’s crucial to clean the area and inspect the circuit board for any damage. Proper cleanup ensures that the board is ready for new components, while inspection helps in identifying any potential issues.
- Common Challenges: Desoldering can pose challenges such as stubborn solder joints, risk of overheating, or potential damage to the board. Understanding these challenges and employing appropriate techniques is essential for successful desoldering.
Simple Soldering Projects for Beginners
LED Circuit on Perfboard
Building a basic LED circuit on a perfboard is an excellent introductory soldering project for beginners. It involves soldering resistors, LEDs, and connecting wires to create a functional LED circuit that illuminates when powered.
- Perfboard
- Resistors
- LEDs
- Soldering Iron
- Solder
- Wire Cutters
- Battery or Power Source
- Prepare the Perfboard: Cut the perfboard to the desired size and layout the component placement.
- Place the Components: Position the resistors and LEDs on the perfboard according to the circuit diagram.
- Solder the Components: Use the soldering iron to solder the resistors, LEDs, and wires to the perfboard, ensuring a secure connection.
- Connect the Power Source: Attach the power source and test the LED circuit for illumination.
By following this detailed guide, beginners can gain hands-on experience with soldering while creating a functional and illuminating LED circuit on a perfboard.
Making a Basic Arduino Shield
Creating a basic Arduino shield involves soldering electronic components onto a prototyping shield to expand the capabilities of an Arduino board. This project introduces beginners to soldering headers, capacitors, and other components to enhance their Arduino projects.
- Understanding Arduino Shields: Arduino shields are expansion boards that can be plugged into Arduino boards to extend their capabilities. They are designed to fit perfectly onto an Arduino board, providing additional functionalities such as GPS modules, motor drivers, and more.
- Choosing the Right Components: When designing a basic Arduino shield, it’s essential to select the right components based on the intended functionality. This may include resistors, LEDs, sensors, or other electronic elements.
- Design Considerations: Before soldering the components onto the prototyping shield, it’s important to plan the layout and connections. Understanding the electrical requirements and ensuring proper spacing for each component is crucial for the shield’s performance.
- Soldering Techniques: Beginners will benefit from learning various soldering techniques such as through-hole soldering, surface mount soldering, and desoldering. Each technique has its advantages and specific applications in Arduino shield development.
- Testing and Iterating: Once the components are soldered onto the shield, it’s essential to test the connections and functionality. Iterative testing and troubleshooting are key to ensuring that the shield performs as expected.
- Expanding Arduino Projects: By creating a basic Arduino shield, beginners can expand their projects to include more sophisticated functionalities. This hands-on experience lays the foundation for future electronics projects and experimentation.
Intermediate Soldering Projects
Temperature-Controlled Soldering Station
A temperature-controlled soldering station is an essential tool for electronics enthusiasts who want to engage in precision soldering tasks. This station allows users to regulate the temperature of the soldering iron, ensuring that it remains at the optimal level for different soldering applications.
Here are some key components and features that are typically found in a temperature-controlled soldering station:
- Temperature Control Unit: The heart of the soldering station, this unit enables users to set and monitor the temperature of the soldering iron. It may include a digital display for accurate temperature readings.
- Soldering Iron: A high-quality soldering iron with a temperature sensor and heating element. It is designed to maintain the set temperature and provide consistent heat during soldering tasks.
- Stand and Holder: A stable stand and holder for the soldering iron, ensuring safe storage and easy access during work.
- Customizable Settings: Some advanced soldering stations allow users to customize temperature profiles, sleep settings, and other parameters for enhanced control and efficiency.
Building a temperature-controlled soldering station involves a combination of assembling electronic components and creating a custom enclosure. Here’s a brief overview of the construction process:
- Assembling Electronic Components: This stage includes the integration of the temperature control unit, soldering iron, and related circuitry. Careful attention to wiring and component placement is critical for optimal performance.
- Custom Enclosure Fabrication: Crafting a suitable enclosure for the soldering station involves considerations such as heat dissipation, ergonomic design, and easy access to the soldering iron and controls. Materials like metal, plastic, or wood can be used for the enclosure, depending on the user’s preferences and requirements.
Furthermore, the use of a temperature-controlled soldering station offers several benefits:
- Precision Soldering: The ability to regulate and maintain the soldering iron’s temperature allows for precise and clean soldering joints, especially on intricate electronic components.
- Component Protection: Controlling the heat applied to sensitive components reduces the risk of damage during soldering, enhancing the reliability of electronic assemblies.
- Enhanced Safety: Advanced safety features in temperature-controlled stations, such as auto-sleep modes and thermal runaway protection, minimize the risk of accidents and equipment damage.
Overall, a temperature-controlled soldering station is a fundamental tool for individuals looking to elevate their soldering capabilities and achieve professional-quality results in their electronics projects.
Building a Digital Thermometer
Building a digital thermometer is an exciting intermediate project that not only enhances your soldering skills but also provides practical experience with temperature sensors and display modules. Let’s dive deeper into the process of assembling a digital thermometer and explore the components and steps involved.
- Temperature sensor module
- Microcontroller (such as Arduino or ESP8266)
- Liquid crystal display (LCD)
- Power source (battery or USB power)
- Electronic components (resistors, capacitors, etc.)
- Enclosure for the thermometer
The assembly of a digital thermometer involves the following key steps:
- Preparing the Components: It’s important to ensure that all the components are in working condition and appropriate for the project’s specifications.
- Soldering the Circuit: Solder the temperature sensor, microcontroller, and display module onto a prototyping board according to the circuit diagram. Pay attention to the proper connections and component placements.
- Programming the Microcontroller: Write the code to read data from the temperature sensor and display it on the LCD. This step involves using appropriate libraries and defining sensor calibration if necessary.
- Testing and Calibration: After assembling and programming, test the thermometer in various temperature conditions to ensure accuracy. Calibrate the sensor if required to improve precision.
- Finalizing the Enclosure: Once the thermometer is fully functional, secure it in an enclosure to protect the circuit and provide a user-friendly interface.
A digital thermometer has numerous practical applications beyond its educational value. It can be used for temperature monitoring in home projects, scientific experiments, or even as a tool for HVAC system diagnostics. Moreover, understanding the principles behind temperature measurement and digital display is beneficial for anyone interested in electronics and DIY projects.
Advanced Soldering Projects for Experts
SMD Soldering Techniques
Surface-mount device (SMD) soldering techniques involve soldering small electronic components directly onto circuit boards. Expert-level soldering skills are required to handle tiny components and achieve precise solder connections.
Creating Custom PCBs
Creating Custom PCBs
- Custom PCB Design
- Iterative Prototyping
- Advanced Soldering Techniques
- Component Integration
Designing and soldering custom printed circuit boards (PCBs) allows experts to fabricate intricate electronic circuits tailored to specific applications. This advanced project demands expertise in PCB design, soldering, and electronic component integration.
When creating custom PCBs, the following considerations must be taken into account:
- Choice of Substrate Materials
- Impedance Control
- Embedded Components
- Signal Integrity
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can optimize the performance and reliability of their custom PCB designs.
Troubleshooting and Common Mistakes
Identifying cold joints and overheating
When it comes to soldering, identifying cold joints and overheating is crucial for ensuring the integrity of electronic connections. Both issues can lead to connectivity problems and component damage, making it essential to have a keen eye for their signs.
Cold joints are characterized by a dull or grainy solder appearance. They occur when the solder didn’t properly flow and bond with the metal components, resulting in poor electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. Recognizing cold joints is a key aspect of troubleshooting connectivity issues during soldering projects.
- Common Signs of Cold Joints:
- Dull or grainy solder appearance
- Inconsistent or weak connection
- Prone to breakage under stress
Overheating during soldering can have serious consequences, including damaging the components and creating long-term reliability issues. It’s crucial to carefully monitor the temperature of the soldering iron to prevent overheating.
- Key Considerations for Overheating:
- Understanding the safe operating temperature for the component materials
- Using appropriate soldering iron tips and wattage to minimize overheating
- Employing proper heat dissipation techniques for sensitive components
Correcting solder bridges and splatter
Correcting solder bridges, which occur when solder unintentionally connects two conductive points, requires precise solder removal techniques. Solder splatter, while less common, can be addressed by adjusting soldering techniques and ensuring proper solder flow.
Safety Precautions and Maintenance Tips
When engaging in soldering projects, observing safety precautions is paramount to protect against potential hazards. Some essential safety measures include:
- Proper ventilation to ensure the fumes from soldering are not inhaled
- Handling hot soldering irons with care to avoid burns and injuries
- Using protective gear such as gloves and safety glasses to prevent physical harm
- Ensuring a clear, clutter-free work area to minimize accidents and mishaps
Additionally, maintaining soldering equipment and regularly cleaning soldering iron tips are crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Regular maintenance tasks include:
- Inspecting the soldering iron for signs of wear and damage
- Cleaning the soldering iron tip after each use to prevent oxidation and improve solder flow
- Replacing worn-out or damaged parts such as tips, heating elements, and cords
- Storing the soldering iron and equipment in a dry and safe environment to prevent corrosion and electrical faults
Conclusion
Embark on an exciting journey of exploration and innovation in the realm of soldering iron projects. From mastering fundamental soldering techniques to conquering advanced projects, this article has equipped you with the knowledge, insights, and inspiration to elevate your soldering skills and embark on captivating electronic endeavors. Embrace the world of soldering with confidence, creativity, and a commitment to safety, and witness the remarkable transformation of your electronic hobbyist pursuits.
