What is a Solder Sleeve? Everything You Should Know
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on solder sleeves, where we delve into the functionality, types, applications, advantages, and best practices of this innovative electrical connector. Solder sleeves are a fundamental component in electrical and wiring connections, offering a streamlined approach to creating secure and insulated junctions. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of solder sleeves and provide valuable insights into their utilization across various industries.
Solder Sleeve Explained
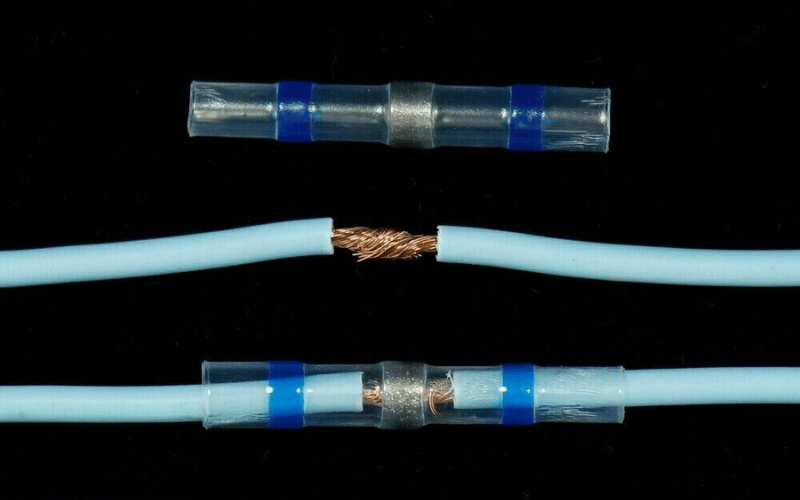
A solder sleeve, also known as heat-shrink solder sleeve, is a specialized heat-shrinkable tube designed with an inner ring of solder. It serves as a versatile solution for creating robust and insulated connections for wiring and cables. When heat is applied, the sleeve contracts, and the solder inside melts, establishing a durable bond while ensuring the electrical components are shielded from moisture and environmental elements. Commonly employed in electronics, automotive, and aerospace applications, solder sleeves offer a convenient and efficient means of joining conductors and maintaining electrical integrity.
- Solder sleeves come in various sizes and dimensions to accommodate different wire gauges and applications.
- They are designed to provide a waterproof and environmentally sealed connection, making them suitable for outdoor and harsh environments.
- The inner solder ring is formulated to create a reliable and low-resistance electrical connection, ensuring minimal signal loss.
- Some solder sleeves feature a transparent heat-shrinkable outer layer, allowing for easy inspection and verification of the solder connection.
- Advanced solder sleeves may include pre-installed flux to enhance solder wetting and bonding, further improving the quality of the electrical joint.
Types of Solder Sleeves
Types of Solder Sleeves
- Standard Solder Sleeves: Designed for general-purpose electrical connections. They are commonly used in household wiring, automotive applications, and electronic manufacturing.
- Waterproof Solder Sleeves: Equipped with added protection against moisture and environmental contaminants, these sleeves are ideal for outdoor or marine applications. They are commonly used in marine electrical systems, outdoor lighting, and underground wiring.
- Corrosion-Resistant Solder Sleeves: Engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them suitable for automotive and aerospace wiring. These sleeves are commonly used in automotive engine compartments, aircraft wiring, and industrial machinery.
- High-Temperature Solder Sleeves: Built to handle extreme heat, ensuring reliability in high-temperature electrical systems. They are commonly used in automotive exhaust systems, industrial ovens, and aerospace applications.
- Insulated Solder Sleeves: Designed to provide electrical insulation in addition to soldering. They are commonly used in electronic devices, control panels, and power distribution systems.
- Heat-Shrink Solder Sleeves: Utilize heat-shrink technology for a secure and waterproof seal, ideal for outdoor and marine applications. They are commonly used in harsh environmental conditions, underground electrical systems, and marine electrical connections.
How Solder Sleeves Work
Solder sleeves function by utilizing heat to create a secure bond between electrical conductors. This heat-activated solder and adhesive-lined sleeve make the process of connecting wires quick and easy. The solder sleeve works by encapsulating the connection within the sleeve, providing both electrical insulation and mechanical protection. Here’s an in-depth look at how solder sleeves work:
- Preparation: Before using a solder sleeve, it’s essential to ensure that the wires to be connected are stripped, cleaned, and properly aligned.
- Placement: The solder sleeve is positioned over the joint, ensuring that both wires are fully inserted into the sleeve.
- Heating: Using a heat gun, the solder sleeve is heated, causing it to shrink and the solder inside to melt. As the solder melts, it flows to create a secure electrical connection between the wires.
- Cooling: After heating, the assembly is allowed to cool, solidifying the connection and creating a watertight seal.
Advantages of Using Solder Sleeves
Advantages of Using Solder Sleeves
Solder sleeves offer a multitude of advantages that make them a preferred choice in various industries.
Enhanced Reliability: Solder sleeves provide a robust and durable connection that ensures long-term reliability in various applications. The seamless fusion of the solder and insulation creates a strong bond that resists corrosion and withstands environmental influences, making it an ideal choice for critical connections.
Time-Saving: The streamlined process of using solder sleeves reduces installation time and labor costs, making it an efficient solution for production environments. This not only improves productivity but also minimizes the margin for error, resulting in consistent and reliable connections.
Environmentally Friendly: Solder sleeves eliminate the need for harmful chemicals, such as flux, leading to a greener and safer soldering process. This eco-friendly feature aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices and reduces the environmental impact of soldering operations.
Effective Insulation: Solder sleeves offer excellent insulation properties, safeguarding the connection from environmental factors and preventing electrical mishaps. This insulation capability ensures that the connection remains stable and secure, even in challenging conditions, enhancing the overall safety and performance of electrical systems.
Versatile Application: Solder sleeves can be used in a wide range of industries, including aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications, showcasing their adaptability and versatility. Whether it’s for wire splicing, cable repair, or component installation, solder sleeves provide a reliable and adaptable solution that meets the diverse needs of modern engineering and manufacturing.
Disadvantages of Using Solder Sleeves
When considering the drawbacks of using solder sleeves, it is important to delve into the specific limitations that users may encounter. These limitations include:
- Precision Requirement: Solder sleeves demand meticulous attention to positioning and heat application to achieve the desired results. Any deviation from the precise requirements may lead to suboptimal outcomes, emphasizing the need for careful handling during the application process.
- One-Time Use: Once a solder sleeve has been applied, it becomes immovable and cannot be repositioned. This characteristic highlights a lack of flexibility, necessitating thorough planning and precision during the initial installation.
- Specialized Equipment: The implementation of solder sleeves may mandate the use of specialized tools and equipment. This requirement can potentially hinder accessibility and convenience, as it may pose challenges in sourcing or utilizing the necessary resources.
- Material Compatibility: Solder sleeves may not be universally compatible with all materials, necessitating a thorough assessment of material suitability before application. Incompatibility issues can lead to compromised soldering results and may require alternative solutions or materials.
- Complex Application in Certain Scenarios: In specific scenarios, such as tight spaces or intricate configurations, the application of solder sleeves can pose challenges. This complexity demands enhanced precision and expertise to ensure successful and accurate connections, further emphasizing the need for careful consideration of the application environment.
How to Choose the Right Solder Sleeve
When it comes to choosing the right solder sleeve for your specific application, there are several critical factors that must be carefully evaluated to ensure optimal performance and suitability. Let’s delve into a detailed guide on how to choose the right solder sleeve:
- Application Environment: One of the paramount considerations when selecting a solder sleeve is the application environment. It is crucial to thoroughly evaluate the environmental conditions in which the solder sleeve will be used, including factors such as temperature, moisture levels, and exposure to chemicals. By understanding the specific application environment, you can choose a solder sleeve that is perfectly compatible and tailored to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
- Conductor Size: The dimensions of the solder sleeve must harmonize with the conductor size for a proper fit. It is imperative to carefully match the solder sleeve to the conductor size to establish a secure and effective connection. This meticulous approach ensures that the solder sleeve provides optimal insulation and protection for the conductors, leading to a reliable electrical connection.
- Insulation Requirements: Determining the level of insulation required for the solder sleeve is a critical aspect of the selection process. This involves assessing the specific voltage requirements and environmental factors related to the application. For applications demanding a higher level of protection, the use of solder sleeves with heat-shrink insulation can provide enhanced safeguarding against environmental elements, offering greater peace of mind for the longevity of the electrical connection.
- Material Composition: The material composition of the solder sleeve is a fundamental consideration in ensuring its performance and reliability. Components such as solder ring, flux, and heat-shrink tubing wield significant influence on the overall functionality of the soldered connection. Hence, understanding the specific attributes of the materials used in the solder sleeve is crucial for making an informed decision and ensuring a robust electrical connection.
- Compatibility: Compatibility with the materials of the conductors is a non-negotiable factor when selecting a solder sleeve. Close attention must be given to ensure that the solder sleeve is fully compatible with the materials of the conductors, which may include copper, aluminum, and various other metals commonly utilized in electrical and electronic applications. By prioritizing compatibility, you can guarantee a seamless integration of the solder sleeve with the conductors, thereby enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the electrical connection.
Best Practices for Using Solder Sleeves
Utilizing solder sleeves effectively involves adhering to best practices such as:
- Surface Preparation: Ensure that the connectors are meticulously cleaned using a suitable solvent to remove any dirt, grease, or oxides that may hinder a strong bond with the solder sleeve.
- Proper Stripping: Carefully strip the insulation from the wire, ensuring that the exposed area is the appropriate length for the solder sleeve.
- Heat Application: Apply heat evenly and consistently to activate the solder, providing a strong and reliable connection that is sealed against moisture and contaminants.
- Inspection and Testing: After the solder has cooled, inspect the joint for any imperfections, ensuring that the bond is secure and the insulation is intact. Use appropriate testing equipment to verify the integrity of the connection.
- Avoid Overheating: Be cautious not to overheat the solder sleeve, as excessive heat can lead to insulation damage or a weak connection.
Applications of Solder Sleeves
Applications of Solder Sleeves
- Electronics: Circuit board assembly, wire splicing, and component connections.
- Automotive: Wiring harnesses, vehicle electronics, and electrical repairs.
- Aerospace: Avionics, aircraft wiring, and space exploration equipment.
- Marine: Marine electronics, navigation systems, and maritime equipment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, solder sleeves serve as indispensable components in electrical connections, offering a seamless and efficient method for joining conductors while providing insulation against external elements. By understanding the types, functionalities, and best practices of solder sleeves, professionals and enthusiasts can leverage this innovative solution to achieve reliable and durable electrical connections across diverse industries and applications.
